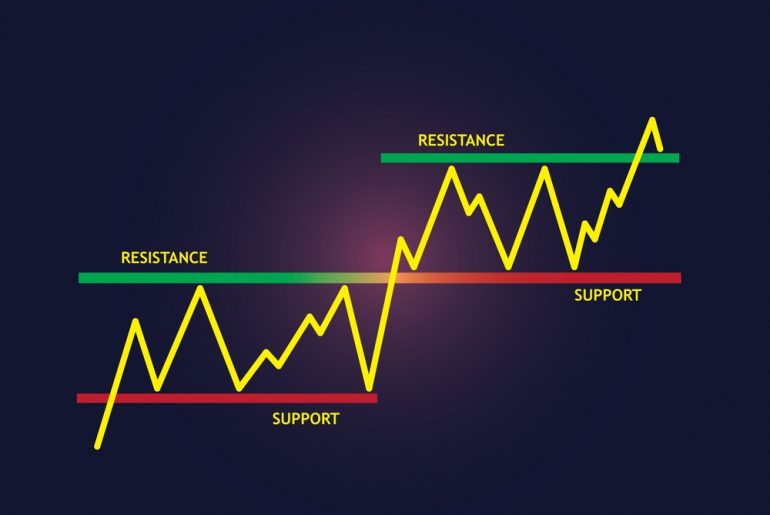
Support and resistance are cornerstones of technical analysis, vitally important in predicting future price movements in financial markets. Traders use these levels to gauge potential entry and exit points, using them as signals for buying or selling assets. Mastering effectively identifying and utilizing support and resistance can provide a significant edge in trading decisions, as they help forecast price reversals or continuations.
This article will explore various strategies based on support and resistance. These techniques are crucial for traders aiming to refine their approach and enhance profitability. Whether new to trading or experienced, understanding these strategies can significantly impact success.
Breakout Strategy
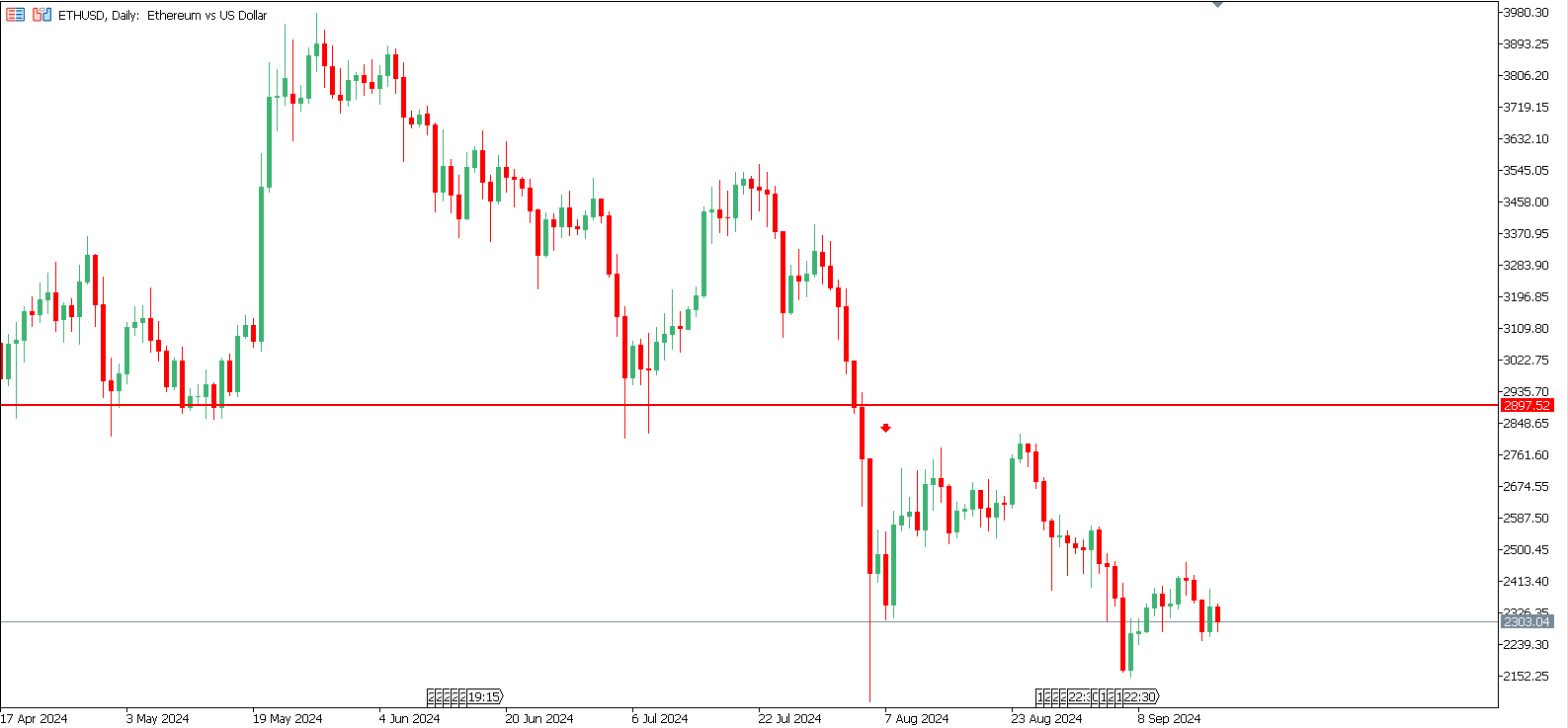
The breakout strategy revolves around identifying moments when the price of an asset moves beyond a critical support or resistance level. This indicates that the price could continue in the direction of the breakout, providing a solid trading opportunity. Traders typically wait for confirmation, such as increased trading volume, before entering a position. This confirmation ensures that the breakout is genuine and not just a temporary price fluctuation.
The breakout strategy is particularly effective in trending markets where momentum pushes prices in one direction. By entering a trade when the price breaks through a significant level, traders can capitalize on the continued movement. However, placing stop-loss orders just below the breakout point is crucial to mitigate risks if the price reverses unexpectedly.
Range-Bound Trading
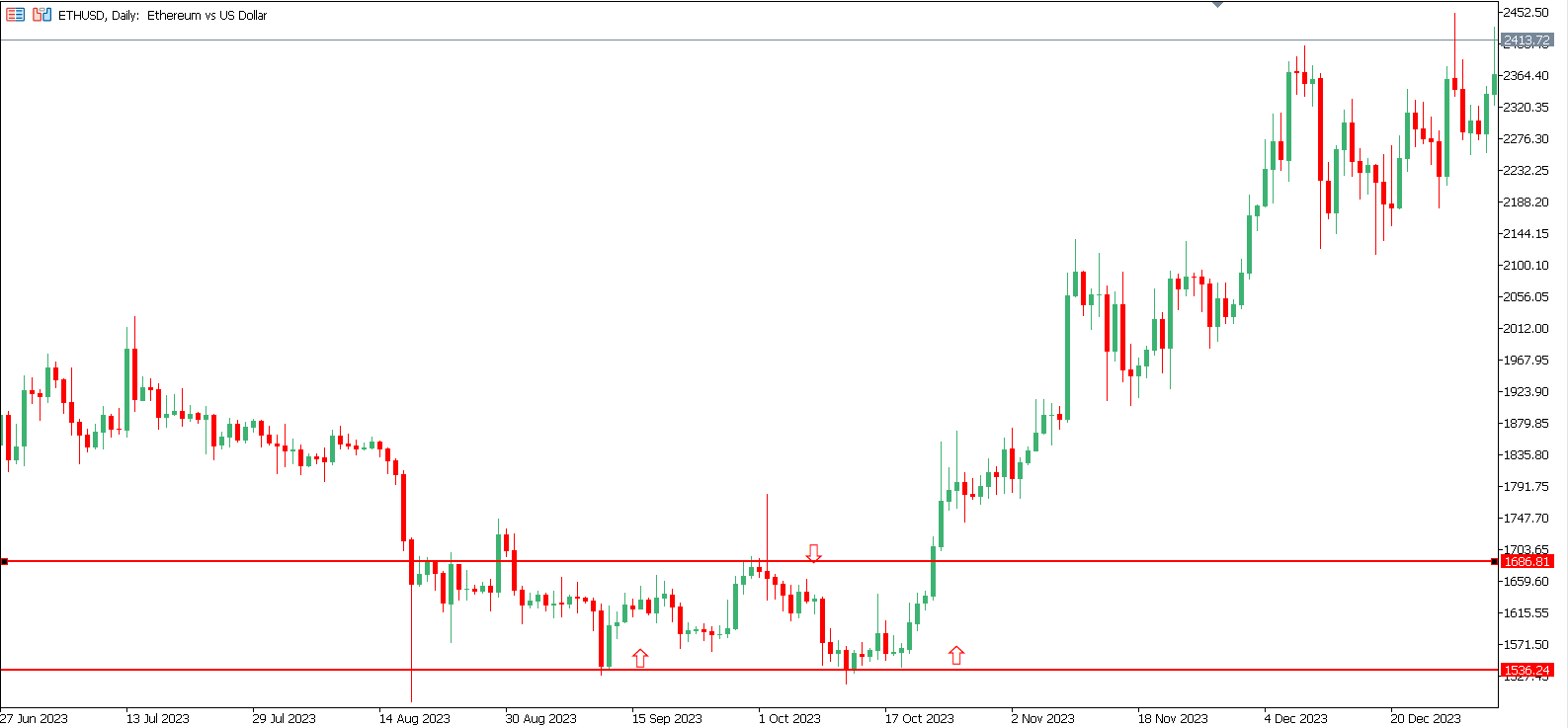
Range-bound trading is a strategy that works well when the price of an asset moves within a defined range, bouncing between support and resistance levels. In such conditions, traders buy near the support level and sell near the resistance, capitalizing on the predictable price movements within the range.
This strategy is ideal for sideways markets without a clear trend direction. It allows traders to take advantage of short-term price fluctuations without needing a significant price breakout. The key to success is identifying a solid range with multiple support and resistance level tests. This ensures that the range is well-established, making it easier to predict future price movements.
Pullback Strategy
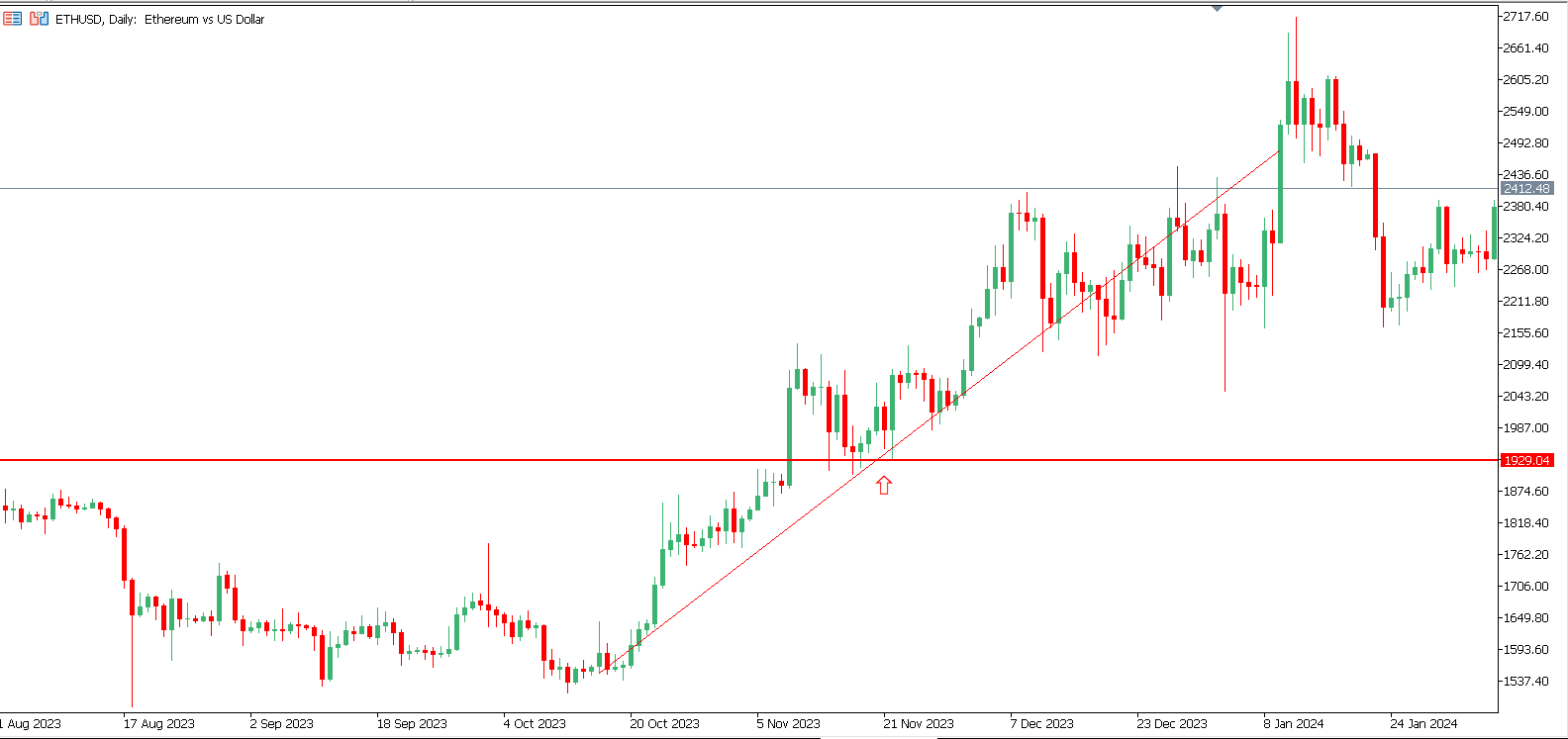
The pullback strategy involves waiting for an asset’s price to return to a support level during an uptrend or a resistance level during a downtrend before entering a position. This temporary reversal allows traders to join a trade at a more favorable price aligned with the prevailing trend. By buying during a pullback in an uptrend, traders aim to capture the subsequent move upward once the pullback is complete.
This strategy requires patience and precision, as entering too early can result in further losses if the pullback extends. Traders often use technical indicators, such as moving averages or Fibonacci retracement levels, to confirm that the pullback has reached a critical level before entering a position.
False Breakout Strategy
The false breakout strategy involves waiting for the price to break through a support or resistance level, only to reverse and move back within the original range. When this occurs, traders take the opposite position to capitalize on the failure of the breakout. This strategy works best in markets with significant volatility, as false breakouts are more likely to occur.
Traders often combine this strategy with technical indicators to identify potential false breakouts. For example, if the breakout occurs at low volume or without a clear momentum shift, it could signal a false breakout. Entering a trade in the opposite direction of the breakout can be highly profitable when timed correctly.
Incorporating support and resistance strategies into your trading approach can provide a solid foundation for making informed decisions and anticipating market movements. Whether focusing on breakouts, range trading, or pullbacks, these techniques help identify key price levels that often lead to profitable opportunities. However, mastering these strategies requires practice, patience, and ongoing education.